|
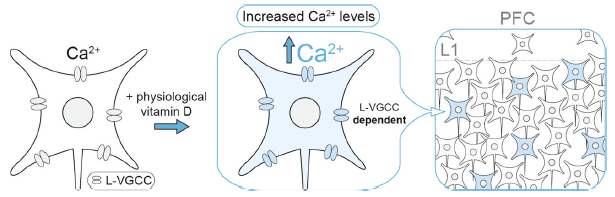
Genetic variants in genes encoding L-type voltage-gated calcium channel (L-VGCC) subtypes are associated with increased risk for schizophrenia. Likewise, epidemiological study has implicated developmental vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for schizophrenia. In the latest study published in Translational Psychiatry, we (led by Prof. John McGrath of QBI, UQ and Aarhus University, Denmark) showed that the active vitamin D metabolite exert a rapid, non-genomic modulation of L-VGCCs in a subset of neurons in developing medial prefrontal cortex in mice. Optimal modulation of L-VGCCs by 1,25(OH)2-vitamin D may therefore contribute to the healthy development of Vitamin D-responsive neurons within the maturing cortical circuits.
|
Synaptic Neurobiology LabArchives
January 2023
Categories
All
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed